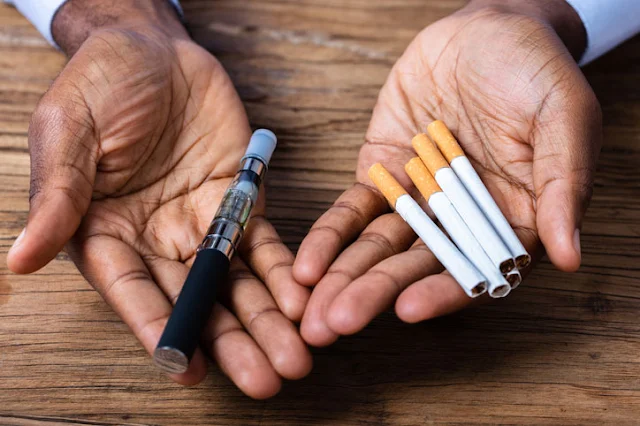
Vaporizer vs Cigarette
Vaporizer vs Cigarette: What You Need to Know
Vaping and smoking are two common ways of consuming nicotine, a highly addictive substance that affects the brain and body. But how do they compare their devices, substances, methods, costs, risks, and benefits?
In this article, we'll explore the differences and similarities between vaping and smoking and provide some evidence-based recommendations for people who want to quit or switch.
- Vaping and smoking differ in the devices, substances, and methods they use. Vaping involves heating a liquid (e-liquid) containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals and inhaling the aerosol (vapor) produced. Smoking involves burning tobacco leaves that contain nicotine and other chemicals and inhaling the smoke that is created.
- Vaping and smoking expose the user to different amounts and types of chemicals. Vaping generally delivers less nicotine and fewer harmful chemicals than smoking. Still, the exact composition and exposure of vaping products vary widely depending on the device, e-liquid, and user behavior. Smoking delivers more nicotine and more than 7,000 chemicals, of which at least 69 are known to cause cancer.
- Vaping and smoking weed have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, convenience, and social acceptability. Vaping may be cheaper, more discreet, and less smelly than smoking, but it may also require more maintenance, pose more technical issues, and face more legal restrictions. Smoking may be more accessible, familiar, and satisfying than vaping, but it may also be more expensive, more harmful, and more stigmatized.
- Vaping and smoking have different short-term and long-term health effects. Vaping may cause immediate symptoms, such as coughing, dry mouth, and throat irritation. Still, it may also reduce some of the harmful effects of smoking, such as tar buildup, carbon monoxide exposure, and oxidative stress. Smoking may cause more immediate symptoms such as bad breath, stained teeth, and reduced taste and smell, but it may also increase the risk of serious diseases such as lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
- Vaping and smoking have different implications for quitting or switching. Vaping may help some smokers quit or reduce their cigarette consumption, but it may also maintain or increase their nicotine dependence or lead to dual use of both products. Smoking may be harder to quit or reduce than vaping, but it may also provide more motivation and support for leaving.
Vaping vs Smoking: What are the Differences?
Vaping and smoking are two different ways of delivering nicotine to the body, but they use many other devices, substances, and methods.
Devices
- Vaping devices, also known as e-cigarettes, are battery-powered devices that heat a liquid (e-liquid) to produce an aerosol (vapor) that the user inhales. Many types and models of vaping devices, such as cigalikes, vape pens, mods, and pod systems, vary in size, shape, design, and features.
- Smoking devices, also known as cigarettes, are paper tubes that contain dried and shredded tobacco leaves mixed with other additives. The user lights one end of the cigarette and inhales the smoke from the burning tobacco. There are also other forms of smoking devices, such as pipes, hookahs, or 510-three batteries like Rick and Morty vape batteries that use different types of smoking and methods of burning.
Substances
- Vaping substances, also known as e-liquids, contain nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals, such as propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, and benzoic acid. The nicotine content and flavor of e-liquids vary widely depending on the brand, product, and user preference. Some e-liquids may contain other substances like THC, CBD, or caffeine.
- Smoking substances, also known as tobacco, are dried and cured leaves of the tobacco plant, which contain nicotine and other chemicals, such as ammonia, formaldehyde, and arsenic. The nicotine content and flavor of tobacco vary depending on the type, origin, and processing. Some tobacco products may contain other substances, such as menthol, cloves, or additives.
Methods
- Vaping methods, also known as vaping behaviors, are the ways that the user operates and uses the vaping device and e-liquid. Vaping methods include the device type, power setting, coil resistance, airflow, puff duration, puff frequency, and inhalation technique, which affect the amount and quality of the vapor produced and inhaled.
- Smoking methods, also known as smoking behaviors, are the ways that the user lights and smokes a cigarette or other tobacco product. Smoking methods include cigarette type, brand, length, filter, ventilation, puff duration, puff frequency, and inhalation technique, which affect the amount and quality of the smoke produced and inhaled.
Vaping vs Smoking: What are the Health Effects?
Vaping and smoking have different short-term and long-term health effects on the body. While vaping may be less harmful than smoking in some aspects, it is not without risks.
Short-term effects
Vaping and smoking can both cause some immediate symptoms and changes in the body, such as:
- Coughing: Vaping and smoking can irritate the throat and lungs, leading to coughing. A 2019 study found that 57.8% of e-cigarette users reported coughing, compared to 76.2% of smokers and 12.4% of non-users.
- Dry mouth: Vaping can dehydrate the mouth, causing dryness, thirst, and bad breath. A 2016 study found that 65.3% of e-cigarette users reported dry mouth, compared to 6.8% of non-users.
- Throat irritation: Vaping and smoking can inflame the throat, causing soreness, pain, and hoarseness. A 2016 study found that 51.2% of e-cigarette users reported throat irritation, compared to 4.5% of non-users.
- Bad breath: Vaping and smoking can affect oral hygiene and microbiome, causing halitosis or bad breath. A 2018 study found that e-cigarette users had higher levels of volatile sulfur compounds, which are associated with bad breath, than non-users.
- Stained teeth: Smoking can stain the teeth and gums, causing yellowing, discoloration, and plaque buildup. A 2017 study found that smokers had significantly higher scores of tooth staining than non-smokers and e-cigarette users.
- Reduced taste and smell: Smoking can impair the senses of taste and smell, making food and beverages less enjoyable. A 2014 study found that smokers had lower scores of taste sensitivity than non-smokers and e-cigarette users.
Long-term effects
Vaping and smoking can both increase the risk of developing chronic and life-threatening diseases, such as:
- Lung injury: Vaping can damage the lungs, causing inflammation, scarring, and fluid buildup. A 2019 outbreak of vaping-associated lung injury VALI) affected more than 2,800 people and caused 68 deaths in the United States. The CDC identified vitamin E acetate, a thickening agent used in some THC-containing e-liquids, as a likely cause of EVALI.
- Cancer: Smoking can cause cancer in various parts of the body, such as the lungs, mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver, kidney, bladder, cervix, and blood. According to the CDC, smoking is responsible for about 30% of all cancer deaths in the United States. Vaping may also increase the risk of cancer, as some e-liquids contain carcinogens, such as formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and nitrosamines.
A 2018 study estimated that e-cigarette use could result in 1.6 to 6.6 additional cases of cancer per 100,000 users over a lifetime.
- Heart disease: Smoking can damage the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. According to the CDC, smoking is a significant cause of cardiovascular disease, accounting for about 20% of all deaths from heart disease in the United States. Vaping may also harm the cardiovascular system, as nicotine and other chemicals can raise blood pressure, heart rate, and inflammation.
A 2019 study found that e-cigarette users had a 34% higher risk of heart attack, a 25% higher risk of stroke, and a 55% higher risk of depression or anxiety than non-users.
- Addiction: Vaping and smoking can both cause addiction, a chronic brain disorder that makes it hard to quit or reduce the use of nicotine or other substances. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that regulates pleasure and reward.
A 2015 study found that e-cigarette users had similar levels of nicotine dependence as cigarette smokers. That dependence was higher among those who used more advanced devices, higher nicotine concentrations, and more frequent puffs.
Vaping vs Smoking: What are the Recommendations?
Vaping and smoking are both harmful to health, and the best option is to avoid or quit both. However, some people may use vaping as a way to stop or reduce smoking or as a less harmful alternative to smoking. Here are some recommendations for people who want to stop or switch from vaping or smoking:
- Seek professional help: Quitting or switching from vaping or smoking can be challenging, especially without proper guidance and support. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider, such as a doctor, nurse, or pharmacist, who can offer advice, resources, and treatment options. Some examples of treatment options are nicotine replacement therapy NRT, such as patches, gums, lozenges, inhalers, or sprays; behavioral counseling, such as phone, online, or in-person services; and medication, such as bupropion or varenicline.
- Seek personal support: Quitting or switching from vaping or smoking can also be easier with the help of family, friends, and peers, who can provide emotional, social, and practical support. Some examples of personal support are joining a quit-smoking program, such as Smokefree.gov, enlisting a quit buddy, such as a friend, partner, or co-worker, and informing others, such as relatives, neighbors, or colleagues, about the quit or switch plan.
- Make a plan: Quitting or switching from vaping or smoking requires planning and preparation, as well as setting realistic and specific goals. Some examples of making a plan are choosing a quit or switch date, such as a birthday, anniversary, or holiday; identifying triggers, such as stress, boredom, or social situations; and coping strategies, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies, and tracking progress, such as using a calendar, app, or journal.
If you decide to switch from smoking to vaping, we suggest choosing devices that exactly fit your needs. Looking for perfect devices is challenging. We recommend devices with MTL puffs. Disposable vape devices like HQD Cuvie Air are the perfect choice.



%20(1).png)






